Human resources are the most valuable assets for any business organization. In order to make fuller utilization or benefit of the available human resources, an organization must have a HR Planning process (HRP). The process of Human Resources Management strategies with proper planning ensures that the organization cannot operate effectively with any manpower surpluses or shortages in the organization.
HR Planning is a continuous and systematic process that should be carried out by the HR department of an organization to ensure the creation of the best fit of the employees to the job roles as well as to the organizational culture and that the right candidate for the right job at the right time is ensured.
Table of Contents
Reasons behind Human Resource Planning:
Talent Management:
HR Planning can help organizations to build effective Talent Management strategies. It involves identifying prospective employees and assigning them targeted development opportunities to help them reach their full potential.
Strategic Decision making
HR Planning provides valuable insights into the workforce and can inform strategic decision-making. For an instance, understanding the current workforce and anticipating their future needs helps organizations make informed decisions about organizational structure, resource allocation, and strategies.
Targeted Training and Employee Development
HR Planning can help businesses identify skill gaps and provide targeted training and development opportunities for their employees. Leading to increased employee satisfaction and motivation, which can ultimately improve productivity and performance.
Future Workforce Needs
HR Planning helps businesses anticipate and also address their future workforce needs. Conducting a thorough analysis of the workforce and forecasting their future needs help organizations to take proactive steps. Therefore, this ensures they have the right talent and resources to meet their organizational goals.
Risk management
HR Planning can help organizations mitigate the risks associated with workforce disruptions, labor shortages, and changes in labor laws and regulations. For example. anticipating risks and developing contingency plans can prepare organizations to handle potential challenges
Managing workforce costs
Effective HR Planning can help organizations manage their workforce costs by avoiding overstaffing or understaffing. Additionally, it allows them to identify opportunities to optimize their workforce structure and performance.
Succession Planning
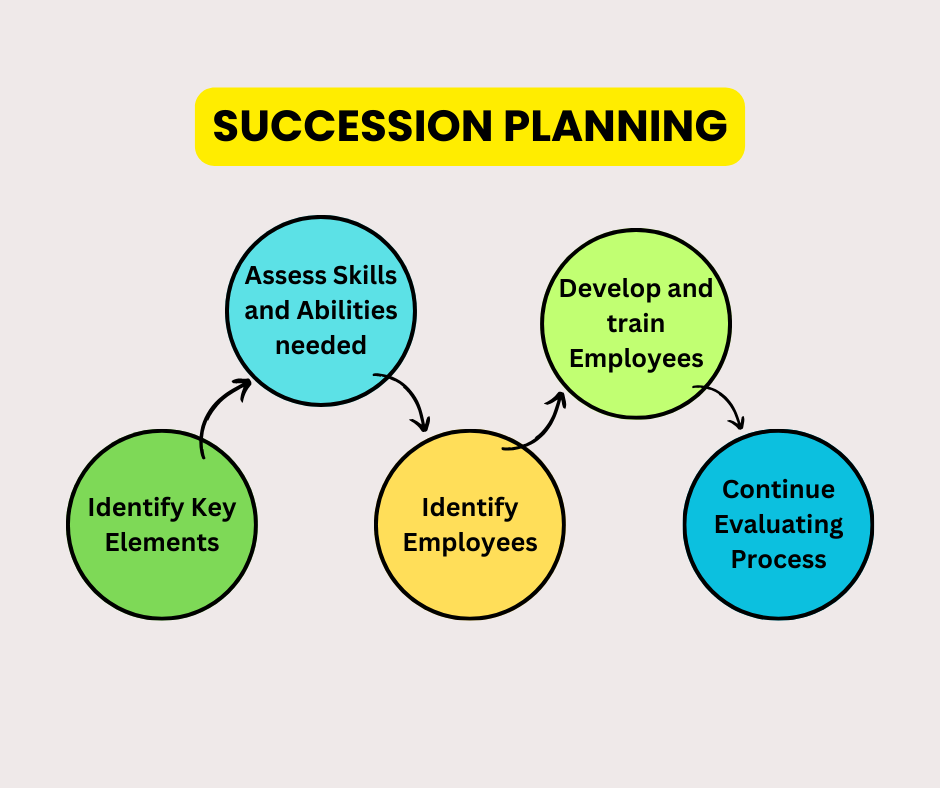
By identifying critical roles and the competencies required for them, HR Planning can help organizations zero in on and, also, develop potential successors, facilitating a smooth transition of leadership and continuity in business operations.
By identifying critical roles and the competencies required for them, HR Planning can help organizations zero in on and, also, develop potential successors, facilitating a smooth transition of leadership and continuity in business operations.
Employee Engagement and Retention
Effective HR Planning can help organizations create a positive work environment, and not just attract but retain top talent, promoting employee engagement and satisfaction.
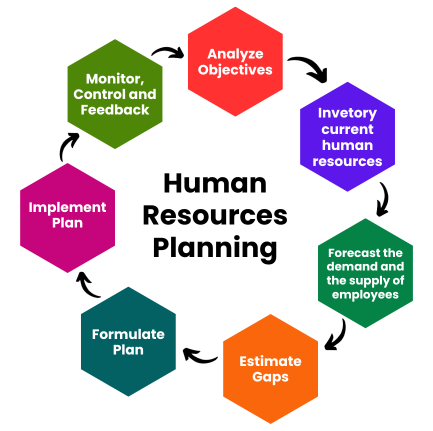
HR Planning Steps (THE ROADMAP)

1. Identify and Analyze organizational goals.
Organizational Goals identification refers to the extent that an organization’s members share the same goals, mission, and values. Organizations are complex entities with different ideas, values, visions, dreams, departments, personalities and departments, making each one of them unique. The overall goal of the organization is to embrace the uniqueness.
Organizational Goal Analysis refers to the evaluation of how solid the mission is, that is, how strong or constructive the goal can be for the entire organization.
It can be executed in the following ways:
● Starts with the identification of the objectives of the different departments in the organization
● Management, marketing, production, finance, sales can have different objectives and specific
expectations related to human resources.
● gives the idea about the work to be done in the organization.
● Identify and analyze the changes that will be necessary for the future of the organization.
For an instance, “Open 500 branches across the country” is a considered long-term goal for a bank; So an efficient HR Planning requires identifying this arousal of goal and analyzing if this major goal is aligning with the personal goals of the other departments of the bank like the finance, marketing, HR sections, say.
Challenges Faced in the identification and analysis:
- Interdepartmental parallelism of goals.
- Intradepartmental parallelism of goals.
- Irrelevance in terms of budget.
- Unattainable and unrealistic missions.
2. Evaluate the status of current workforce.
Current workforce evaluation is a mechanism of analyzing the performance or output of the existing employees based on their input, competencies, skills, risk taking abilities, pro action and other parameters. It is vital to track the current status primarily before attending to the upcoming ones.
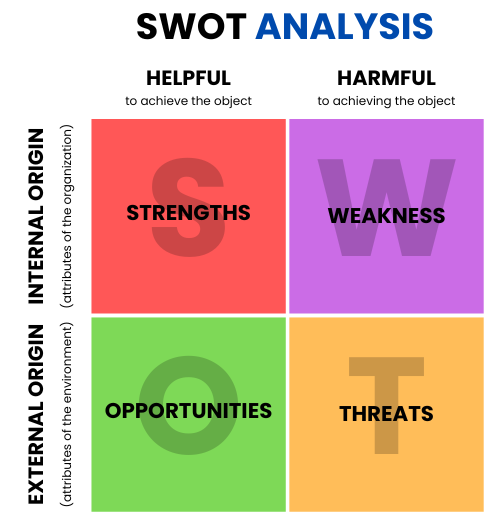
- Assess where the organization’s workforce currently stands by SWOT ANALYSIS.
SWOT analysis is monitoring the manpower on the basis of following heads: – Their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and the threats so as to understand which direction they can be pushed forward in for effective utilization in the organization.
- Questions to consider:
1. Do you have the right number of experienced employees?
2. Which skills at what levels do you already have on board with your existing staff?
3. How do employees rank in performance evaluation data?
To investigate the following variables,
- HRIS in workplace planning.
Provides competitive advantage when HR in workforce planning is facilitated by HRIS, as HRMS can assist in recognizing competent
employees, with a statistical overview.
HRIS Electronic Recruiting facilities reduce organizational cost.
HRIS ensures timely succession planning. - Past performance Reviews
- Employee Self Evaluations.
For an instance,
A training institute wants to evaluate its existing trainer on her training competency. So, with the help of a performance Management scorecard, the current employee’s skill set can be evaluated in terms of KEY RESPOSIBILITY AREAS AND KEY PERFORMANCE INDICES informally in 2 weeks to decide if the training can be invested on her or the company needs to find fresh personnel.
3. Assess Performance Gap:
A Gap Analysis is a critical assessment process which allows you to compare current employee quantity and skill levels with what will be needed to meet the organization’s goals as in, BENCHMARKING.
It measures actual against expected results to identify suboptimal or missing strategies, processes, technologies, or skills. Use the results of a gap analysis to recommend actions that your company should take to meet its goals.
This method involves the following processes:
- Compare current employee quantity and skill levels with what will be needed to meet the organization’s goals. This method involves:
- Recognizing the current workforce status.
- Ascertaining what the ideal situation looks like.
- Identifying where the current lapses exist.
It can be strategic as well as optional. When strategic, it can focus on the overall organization and the planning and execution at that level, or it can be operational and focus on the day-to-day work of a team or department. Since both methods are based on real-world situations, there’s no need to make assumptions.
For an instance,
- New Product Launch: After a company launches a new product, they might do a gap analysis to determine why sales didn’t meet forecasts.
- Productivity: When a factory’s productivity is not meeting expectations, targeted customer needs, or the set of business requirements that were laid out a gap analysis can help determine what process to fix.
- Supply Management: If a hospital finds itself running short of supplies on a regular basis, they could perform a gap analysis to identify the reason why.
- Sales Performance: A manufacturer can look at the sales performance of their catalog of products to make sure they are producing the right mix, and use the result to maximize their production–possibility frontier.
- Individual Assessment: A team leader at an accounting firm can have each member perform a gap analysis on themselves, and use those results not only to find targets to improve each person’s performance, but also to draw out the best practices that everyone can adopt.
- Product Evaluation: A software company might perform a gap analysis of their product to ensure that all features and functions outlined in the business requirements are present and working as expected.
4. Forecast Demand and Supply of Human Resources:
The human resources required at different positions according to their job profile are to be estimated which constitute the demand for Human resources.
The available internal and external sources to fulfill those requirements are also measured, which constitute the supply of personnel.
- Based on the objectives of the different departments of the organization and the inventory of the available resources,
- Questions to consider:
1. Do we need to add more employees for new roles? If so, where from? How many? Full-time or part-time?
2. Does the market have an adequate supply of potential employees?
3. Do we need to train and develop our existing employees for reallocation? Which ones?
4. Are we drawing on the expertise of current employees sufficiently?
For an instance, training institute XYZ wants to assess its workforce demand and supply needs.
Now, for the demand side, XYZ should work on the following questions:
- What do we plan on selling this year?
- What is the market opportunity? Is it growing? Is demand increasing or flat?
- Do we have new products that are entering the market while others are leaving the market?
- What are our competitors doing? Who’s trying to take the customer base away from me?
Now for the supply side, - Are the materials that we need available?
- Do we have the ability to manufacture the products?
- Do we have the talent needed to build the product?
- Do we have the talent needed to provide services to our customers?
- Is the talent in short supply?
5. Formulate the HR Action Plan:
Forming a framework of action plans refers to building a stepwise execution of plans documentation to take careful consideration of the sequence, accuracy and duration of the planned activities.
- Accordingly, the plan to be finalized, either for new recruitment, training, interdepartmental transfer in case of deficit of termination,
- Or voluntary retirement schemes and redeployment in case of surplus.
- Human resource action plan that aligns with your organization’s overall strategy.
- Should take into account all the analyses you’ve completed and include talent strategies to match the supply and demand
- Plan can start with the theoretical concept of transforming the company from X to Y and then name the step-by-step approach that HR will facilitate.
- Include developing methods to enhance specific strategies to take you to the ideal stage.
- Typical areas of focus: recruiting, on boarding, training, benefits, performance management, remote/flexible work options, and company culture.

For an instance,
In the context of recruitment, XYZ Pvt Ltd needs to hire 3 candidates for the position of academic counselors (2) and 1 digital Marketing Executive within 15 days. Now, since it’s already a SMART goal,
First 4 steps of the plan of action have been lined down below:
1. Plan creating respective JDs.
2. Plan Posting the Job vacancies on various sources as per planning.
3. Plan the Screen the pool of candidates received, also, reaching out to those whose resume goes with the position and screening them.
4. Plan to Schedule a telephonic/in person interview with the shortlisted ones.
However, few things to keep in mind while chalking out a POA:
● no one-size-fits-all content for a strategic HR plan
a. Each organization’s strategy will be unique, depending on its goals and the type of business it is.
b. A small startup’s plan would include completely different factors than that of a multi-national corporation.
c. One company may need to start with an enhanced recruitment program to find a certain number of highly skilled employees with specialized knowledge.
d. Another company might be able to begin with training its current staff.
● Focus on integrating it with strong company-wide communication.
● Be prepared for some resistance to change that may occur within frontline employees and management
6. Implement the plan:
Implementation is the final or ultimate carrying out or execution of the formulated list of tasks.
- After formulation.
- Should be aligned with the goals and objectives of the organization as well as those of each department of the organization.
- Human resources are allocated according to the requirements.
- Inventories are updated over a period.
For an instance,
In the context of recruitment, XYZ Pvt Ltd needs to hire 3 candidates for the position of academic counselors (2) and 1 digital Marketing Executive within 15 days. Now, since it’s already a SMART goal, first 4 steps of the ACTUAL action have been lined down below:
1. Plan creating respective JDs.
2. Plan Posting the Job vacancies on various sources as per planning.
3. Plan the Screen the pool of candidates received, also, reaching out to those whose resume goes with the position and screening them.
4. Plan to Schedule a telephonic/in person interview with the shortlisted ones.
7. Monitor, Control and Feedback:
Monitoring in HR Planning is referred to the assessing and reassessing of every activity to check on the current state of how appropriate it is being done as per the intention and also to retaliate or take directive measures if not.
● Should be monitored strictly to identify the deficiencies and remove it.
● The feedback at each level should be obtained to measure any defects in the implemented human resources plan.
● Comparison between the human resource plan and its actual implementation to be done to avoid disarray.
● The necessary controls should be put in place
For an instance,
There is a project management team in pharmaceuticals company Phoenix Pvt Ltd, consisting of the members of the project team who are directly involved in project management activities. These are the do-ers on the team.
To monitor and control TO BE DONEs:
● ensuring the people who are assigned and allocated to the project (your Project Management
Team, as described in your HR Management Plan) are available as planned
● Monitoring the planned Vs actual utilization of these people and taking corrective action as
necessary
Without HR Planning in an organization?
The consequences of not having a human resources (HR) plan or strategy can be significant and far-reaching, impacting the organization and its employees in many ways. Some of the consequences include:
1. High Employee Turnover: Without an HR strategy in place, organizations may experience high employee turnover as employees may become disengaged , demotivated and look for better opportunities elsewhere.
2. Lack of Talent Management: Without an HR planning, organizations may not have a comprehensive approach to attracting, retaining and developing talent, which can lead to a shortage of skilled employees and a lack of capacity to meet business needs.
3. Poor Employee Morale and Engagement: Organizations without HR planning may not have effective methods for addressing employee grievances, managing conflicts or fostering a positive workplace culture. This can result in low employee morale and engagement.
4. Legal and Compliance Issues: Organizations that lack HR plans are more vulnerable to lawsuits and regulatory compliance issues, such as discrimination, harassment and health and safety violations.
5. Inefficient Use of Resources: Without an HR planning, organizations may not have effective systems in place for recruiting, training, compensating and promoting employees. This can result in inefficient use of resources and a lack of productivity.
6. Difficulty in Achieving Organizational Goals: Organizations without HR planning may not have the workforce necessary to achieve their goals and may struggle to meet the demands of their customers and stakeholders.
Overall, a well-designed HR planning can help organizations create a competitive advantage by attracting, retaining, and developing a talented workforce, while also ensuring that HR practices are aligned with the organization’s mission, vision and values.
Challenges in HR Planning:
● Cost
HR is not a revenue-producing department. Consequently, budgeting for human resources functions should be carefully considered given other start-up costs and expenses for your organization. The return on investment for your human resources department may not be measurable for quite some time; this means you might need to do more research to get certain programs, such as a new employee wellness initiative or morale-building program.
These programs often have a measurable impact on reducing health care costs and worker attrition, but you might be asked to show numbers to prove this. As your business matures and your human resources department contributes to the dynamics of your workforce, you will realize the return on your investment.
● Educating Top Management
Building a reliable, proficient workforce is going to be the approach you need to watch your business flourish. The inclusion of human resources at the board table may meet with resistance from traditional executives who do not yet understand the value of a human resources expert being involved in the strategic planning of your company.
HR Planning values in an organization operate like sand in an inverted funnel. Hence, it has to begin from the top-level management’s conceptual modification Engagement of senior managerial positions in various HR Planning and OB seminars, workshops is needed to enlighten them on the
importance of such dimensions required to be prioritized to withhold competitive advantage.
● Deep Rooted Staffing Issues.
One of the challenges in HR Planning that you are sure to encounter with staffing is the decision to hire human resources generalists experienced in all areas of human resources or to invest in specialists for each area. For example, generalists focus on tasks such as hiring, training, wellness and benefits. At a small business just starting out, a generalist with a great deal of experience will probably be best until your
company grows to the point where you require additional staff.
This should be taken care of by rigorous discussion sessions with the management, look for the need of the time or moment, consider the constraints and by elimination method, we can certainly choose the one actually required.
To conclude,
HR planning then ultimately translates the organization’s overall goals into the number and types of workers needed to achieve those goals.
Without clear-cut planning and a direct linkage to the organization’s strategic direction, estimating an organization’s human resource needs is reduced to mere guesswork.
