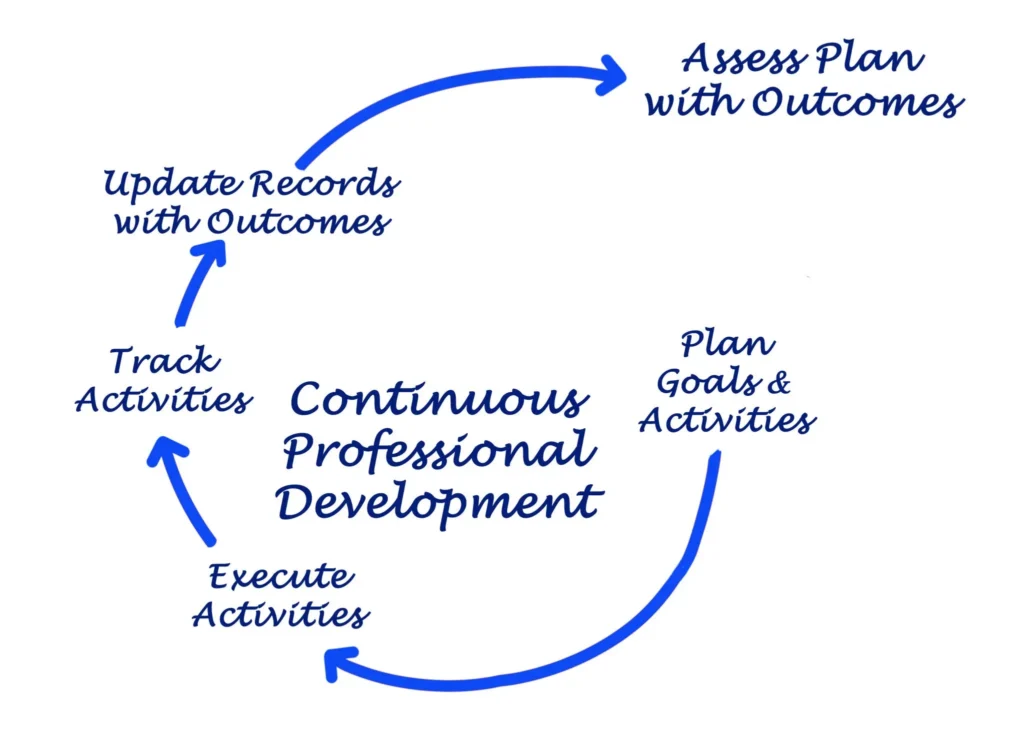
Professional development is a core component of management and organizational behavior. It encompasses a structured process designed to enhance the overall effectiveness and health of an organization.
In every organization, professional development is essential for anyone engaged in a profession. It helps increase an employee’s required skills and aligns them with work objectives over time. Most organizations schedule professional development training annually; however, this process should ideally begin the moment an employee joins the organization.
By receiving this training, employees can help the organization achieve its goals while simultaneously advancing their own career paths. Furthermore, professional development should be reviewed mid-year to assess employee progress and adjust performance parameters.
Professional development is both directly and indirectly linked to organizational behavior. As a representative of your company, your professional conduct significantly impacts the organizational structure. Through positive behavior and highly developed professional skills, you enable the organization to reach its objectives while ensuring your own career success.
Key Pillars of Professional Development
Planned Change
Central to professional development is the process of planned change. This can be described as a thoughtful, systematic effort to positively influence the various elements of an organization. Rather than reacting to issues as they arise, planned change allows an organization to evolve intentionally.

Organizational Culture
Organizational culture is the most critical element of professional development. It directly impacts the daily work environment, defining how employees interact and how professional growth is prioritized.
Organizational Effectiveness
This is one of the most vital objectives of professional development. The primary goal is to elevate performance, efficiency, and individual capabilities to ensure the organization successfully achieves its strategic goals.
Professional Development Interventions & Employee Satisfaction
Numerous research studies indicate that professional development interventions are specifically aimed at increasing employee satisfaction and engagement. When an employee feels the organization is investing in their growth, their commitment to the company typically strengthens.
Core Objectives of Professional Development
The primary goal of professional development is to elevate your career to the next level while simultaneously developing your interpersonal skills. Below are the key objectives:
- Increase Job Satisfaction: Professional development is a proven pathway to higher job satisfaction and long-term engagement.
- Build Confidence: It aims to boost your confidence levels, empowering you to manage complex situations and challenges with ease.
- Skill Enhancement: To improve your technical and soft skills through a structured learning path that aligns with the organizational structure.
- Adaptability and Future-Proofing: To prepare yourself for a changing environment so that you can readily adopt new implementations and innovations as they emerge.
- Career Growth: Following these steps ensures a continuous growth trajectory for your professional life.
Steps and Processes in Professional Development
Professional development is a properly structured process designed to enhance organizational effectiveness and facilitate planned change. This process involves every employee—from top-level management to entry-level staff—to ensure that information is accurate and growth is consistent. Below are the sequential steps of this process:
1. Self-Observation and Employee Diagnosis
The first step for a professional development specialist is to facilitate self-observation and diagnosis for everyone in the organization. This allows employees to provide feedback on their current performance, identifying points for improvement and specific skills required for their future growth.
- Frequency: Self-observation forms should be distributed to every employee twice a year (biannually).
- Action: Forms must be submitted by the specified deadline. Once collected, they are used to classify which specific professional development training is necessary for each individual.
2. Diagnostic Techniques
Various techniques are utilized during the diagnostic phase to gather actionable data:
- Questionnaires and Surveys: These tools collect data regarding employee perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors. They highlight patterns and trends related to organizational issues, such as job satisfaction and leadership communication.
- Interviews: One-on-one interviews provide an opportunity to gain deeper insights from employees at all levels. This helps management understand specific problems and how organizational structures impact individual performance.
- Observation: Observing employees in their working environment is essential for identifying which areas are most critical for development. This direct oversight helps improve overall employee effectiveness.
- Examination of Documents: Reviewing organizational documents—such as performance reports, organizational charts, and policy manuals—helps in understanding the formal structure and highlights specific areas where employees may be lacking support or skills.

3. Planning: The Action Research Phase
Once the diagnosis is complete, the next stage is Action Research Planning. After reviewing all self-observation applications, you must identify the specific skills and development areas required for each employee.
Training needs should be categorized into groups such as technical skills, soft skills, communication skills, and aptitude. Once these categories are established, you can arrange the necessary training sessions.
Key Steps in the Planning Process:
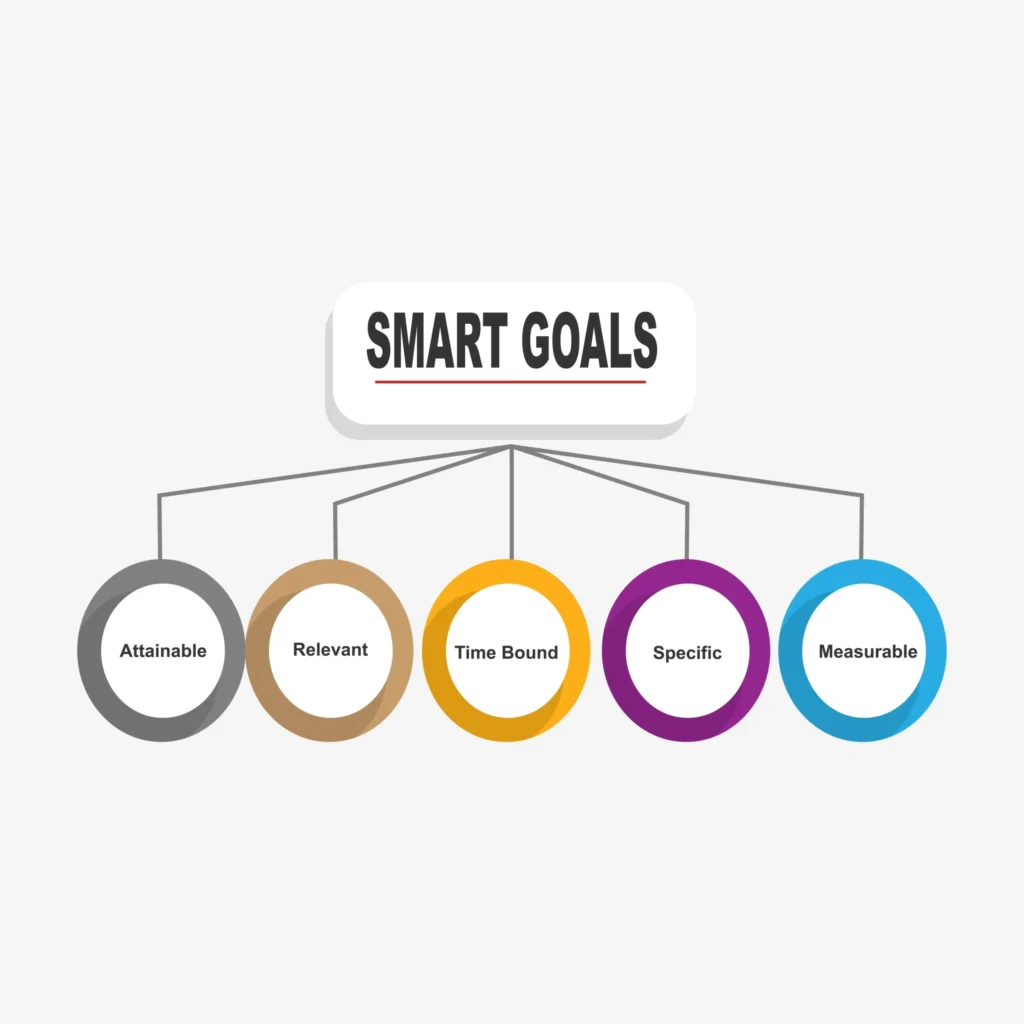
- Set Objectives (SMART Goals): Objectives must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Clear objectives provide direction and ensure the professional development process remains focused.
- Design the Plan: This involves selecting the specific development interventions needed to meet your objectives. Examples include leadership training, team-building activities, and employee engagement initiatives.
- Resource Allocation: The plan should clearly outline the resources required, including the budget, personnel (staff/trainers), and time.
- Timeline: A detailed timeline is essential for tracking progress. It should indicate key milestones and deadlines to ensure the implementation stays on schedule.
- Communication Plan: This ensures that all employees are aware of the expected changes. It should clarify their specific roles, what is expected of them, and the anticipated results.
4. Implementation: Meeting Organizational Needs
Implementation is the execution stage of the planned professional development process. Once the self-observation phase is complete, organizational needs are finalized. It is essential that employees are motivated to embrace this new environment; as they work toward achieving organizational goals, their careers should grow simultaneously.
Examples of Achievement Targets:
- Individual Achievement
- Team Achievement
- Departmental Achievement
Critical Phases of Implementation
1. Execution of Steps
The selected steps must now be implemented according to the established plan. This usually takes the form of structured training sessions, workshops, or hands-on development programs.
2. Managing Change
To ensure a smooth transition and reduce friction during implementation, change management practices must be applied. Addressing employee concerns and facilitating open communication helps minimize resistance to new processes.
3. Progress Monitoring
Once implementation begins, progress must be monitored at every stage. Observations and data should be recorded periodically to track how the changes are taking root and if they are meeting the initial objectives.
4. Adjustments and Flexibility
Professional development requires a high degree of flexibility. Based on the data gathered during monitoring, you must be prepared to make adjustments where necessary. Adaptability is instrumental in ensuring the process yields positive long-term results.
5. Evaluation: Measuring Impact and Success
The evaluation process assesses the effectiveness of professional development interventions and determines if the initial objectives have been met. It allows the organization to refine training and development strategies based on real-world results.
Key Steps in the Evaluation Process
1. Self-Assessment and Supervisor Feedback
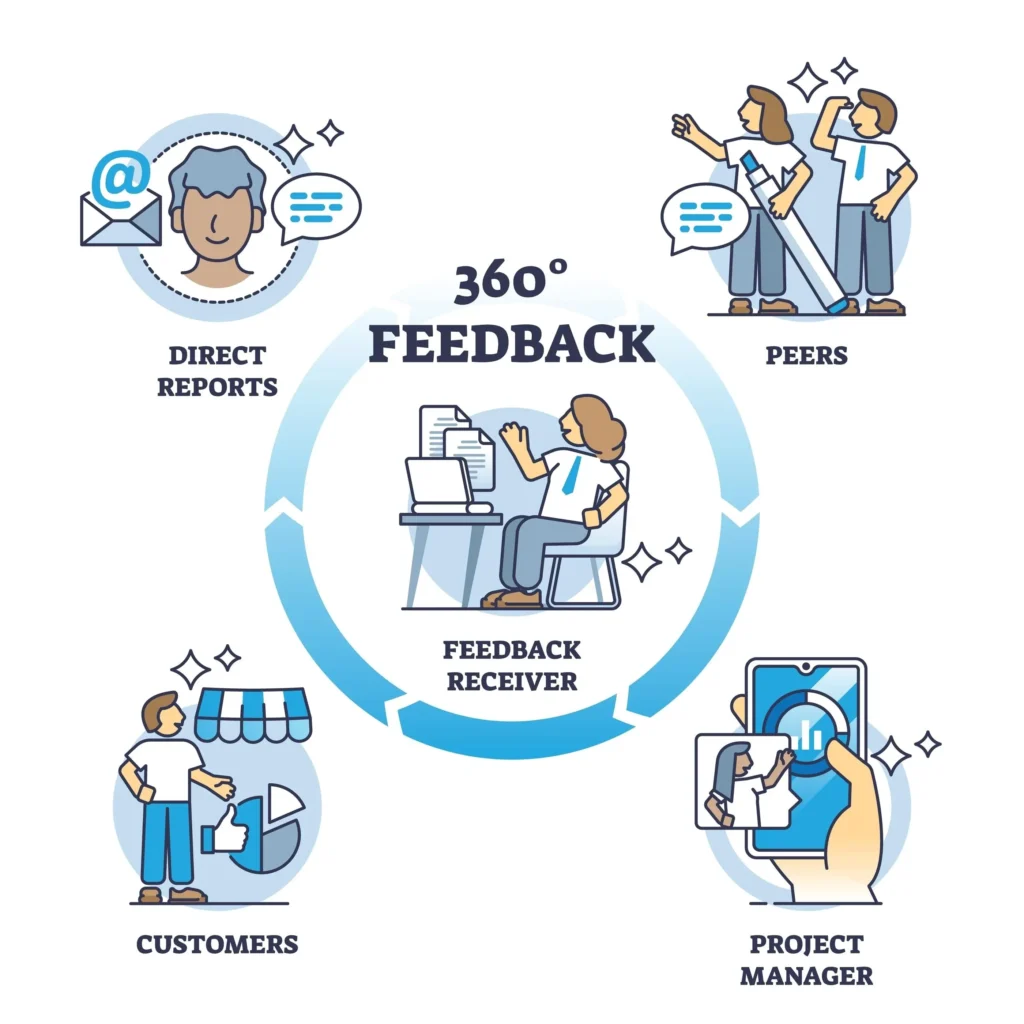
In this step, every employee participates in a self-assessment. To ensure a comprehensive view, the organization utilizes 180-degree or 360-degree feedback forms. This includes feedback from reporting managers and is conducted annually to support the growth of the employee’s professional career.
2. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Every employee should have specific parameters known as KPIs for each KRA (Key Result Area). A KPI is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an employee is achieving their key responsibilities. Without clear KPIs, KRAs cannot be properly identified or measured, making it difficult to track professional development progress.
3. Gathering Feedback
As a professional development specialist, you should collect feedback from every employee in the organization twice a year. Feedback provides more than just information; it is a vital tool for identifying specific areas that require further improvement or additional training.
4. Lessons Learned Documentation
This process involves documenting the entire experience to identify what went well and what could have been handled better. These findings are then archived and applied to future professional development cycles to ensure continuous improvement.
5. Presenting Results
Based on the current development results, you must prepare the next steps for the organization. Evaluating present outcomes is an important process that dictates the future strategy and health of the organization.
6. Sustainability
Sustainability is an ongoing part of the professional development process that ensures long-term success. This element lies outside the formal phases of Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation, as it focuses on maintaining growth over time.
Key Drivers of Sustainability
- Incorporating Change: This involves embedding new practices into the professional culture to ensure they become routine. This is achieved through policy and procedure updates, as well as ongoing training sessions designed to reinforce the changes.
- Supporting Change: Long-term change is sustained through regular communication and a positive support system. Providing consistent encouragement and resources ensures that the transition remains successful.
- Monitoring Long-Term Impact: Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure that changes keep producing the expected results. This prevents the organization from sliding back into old habits and ensures the new processes remain relevant to organizational needs.
- Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Maintaining a supportive environment is necessary for continuous improvement within the organization. This approach increases overall organizational effectiveness and ensures that employees’ professional skills continue to grow.
Key Components of Professional Development
To successfully manage professional development within an organization, several core competencies must be mastered. These components ensure that the PD executive can effectively guide the growth of others.
1. Self-Awareness and Acknowledgement
A fundamental part of professional development is the ability to identify and understand both the strengths and weaknesses of employees. By fostering self-awareness, a PD leader can tailor growth plans that address specific gaps while leveraging an individual’s natural talents.
2. Leadership Qualities
Leadership skills are essential for any Professional Development executive. As a primary representative of the organization’s structure and values, you must model the behavior you expect from others. When conducting training, your leadership style sets the tone for the entire organizational environment.
3. Training and Education
A Professional Development manager must be a lifelong learner. It is vital to stay informed and well-educated on every topic relevant to the organization’s growth. This ensures that the training provided is modern, accurate, and directly applicable to the company’s needs.
4. Mentorship and Coaching
Effective professional development requires providing personalized guidance and support to employees at every level—from entry-level staff to senior management. Acting as a mentor helps build trust and ensures that development is treated as a collaborative journey rather than a top-down mandate.
5. Experiential Learning
Growth often happens best through action. Providing employees with “hands-on” experience through job rotations, specialized projects, and leadership opportunities allows them to apply their skills in real-world scenarios, reinforcing their learning through practice.
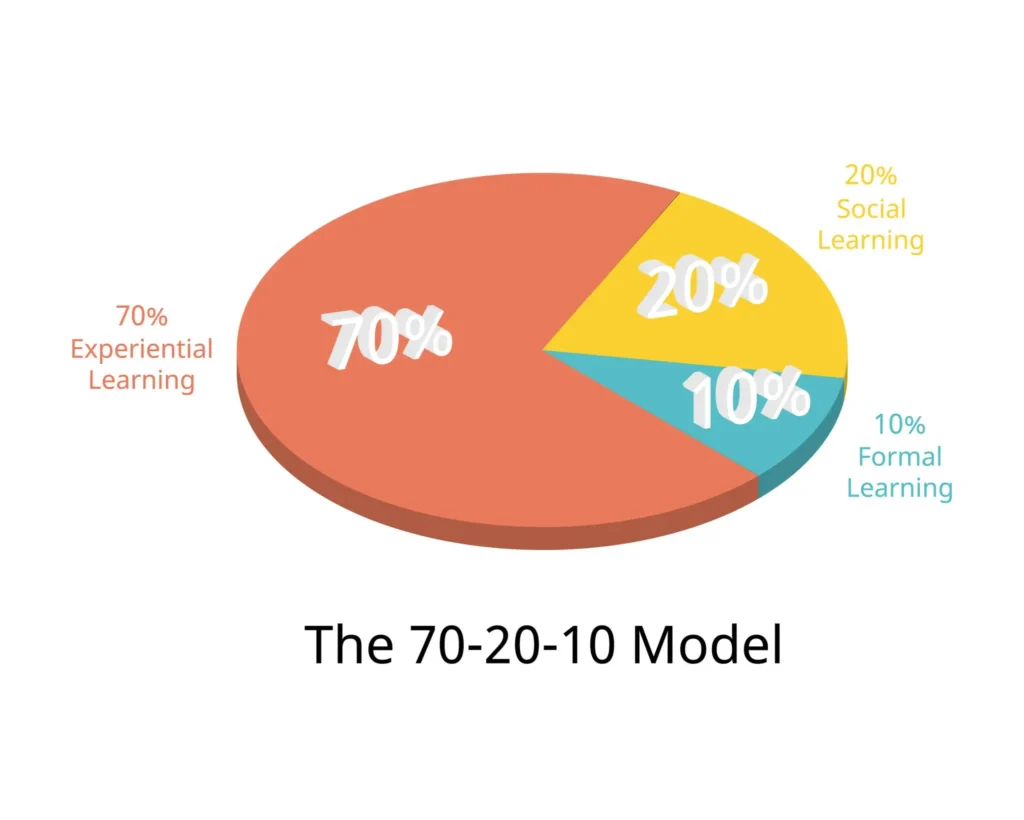
Steps in Professional Development
Professional development steps are purposive actions aimed at enhancing performance and improving the efficiency of an organization. Below are the primary goals of these strategic steps:
1. Build a Competitive Advantage
By innovating and implementing advanced practices within the business, professional development ensures superior customer service and operational excellence. This strategic planning keeps the organization ahead of its competitors.
2. Increase Financial Performance
As employees grow through professional development, their improved efficiency directly impacts the bottom line. This leads to increased revenue, higher profit margins, and greater overall financial stability for the organization.
3. Improve Employee Engagement
Professional development fosters a deeper connection between the staff and the organization. By involving employees in continuous learning and organizational activities, even using animation in engagement in this AI era, you significantly increase their engagement and commitment to their work.
4. Increase Adaptability
A key goal is to enhance the organization’s overall structure, allowing it to respond effectively to market changes. By building a workforce that is ready for change, the organization can gain a significant advantage through increased adaptability and resilience.
Here is the proofread and polished version of the Types of Professional Development Interventions. I have corrected the phrasing and categorized the examples more logically to reflect standard organizational behavior terminology.
Types of Professional Development Interventions
Professional development steps can be categorized into specific interventions designed to improve different facets of the organization.
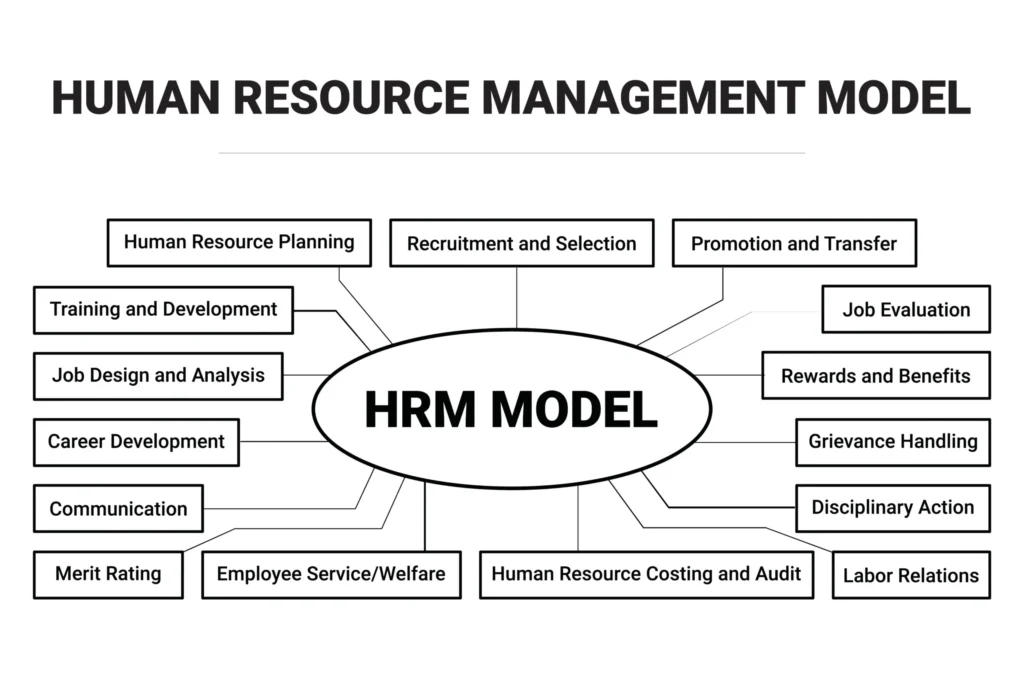
1. Human Resource Management (HRM) Interventions
These interventions focus on improving Human Resource practices to better manage talent and performance. They are designed to resolve issues related to employee growth and organizational health. Key examples include:
- Employee Wellness Programs: Initiatives aimed at maintaining the physical and mental health of the workforce to ensure long-term productivity.
- Talent Development: Identifying high-potential employees and providing them with the resources needed to grow into future roles.
- Training and Development Delivery: Providing structured programs that improve technical and soft skills, directly facilitating career progression.
2. Strategic Change Interventions
Strategic interventions involve large-scale changes to the organization’s overall strategy and structure to gain a competitive advantage. Examples include:
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Integrating different corporate cultures and systems to expand market reach.
- Restructuring: Reorganizing the internal hierarchy or departmental functions to improve efficiency and communication.
- Strategic Planning: Defining the long-term direction of the organization and allocating resources to pursue this strategy.
- Team Building: Strengthening the relationships and collaborative capabilities of groups within the organization.
- Leadership Development: Targeted leadership training for HR, executives, and managers to improve decision-making and organizational influence.
3. Techno-Structural Interventions
These steps are highly useful professional development methods that focus on improving organizational design and the application of technology. By aligning the structure of the organization with the tools available, efficiency is maximized. Key examples include:
- Quality Management: Implementing systems like Six Sigma or Total Quality Management (TQM) to ensure products and services meet high standards.
- Technology Introduction: Integrating new software, hardware, or automated systems and training employees to use them effectively to improve workflow.
4. Human Process Interventions
The primary aim of human process interventions is to enhance interpersonal skills and group dynamics. These interventions are designed to foster better communication and collaboration across all levels. Key examples include:
- Individual Interventions: One-on-one coaching or mentoring sessions focused on personal growth and professional behavior.
- Team Building: Facilitated activities designed to improve trust, cohesion, and collective problem-solving within a specific group.
- Inter-group Relations: Strategies aimed at improving coordination and reducing conflict between different departments or teams within the organization.
Career Development
Professional development is directly linked to career development. It serves as the primary roadmap for employees to achieve their professional goals smoothly. A career development plan is unique to each employee and team member, tailored to their specific situation and requirements. Employees should collaborate closely with their managers to regularly update their development and career paths.
The Importance of Career Development
A career development plan is an essential tool for all employees. It helps maintain motivation through structured planning and clear objectives. Specifically, these plans help employees:
- Set Practical Goals: Establish career milestones that are both realistic and achievable.
- Develop Skills and Knowledge: Identify and acquire the specific competencies required for growth.
- Maintain Motivation: Keep positive energy and focus by seeing a clear path forward.
- Increase Engagement: Boost job satisfaction and commitment to the organization.
- Foster a Positive Culture: Contribute to a healthy and growth-oriented work environment.
Synchronizing Organizational and Career Goals
In a successful organization, professional development and career development impact one another; they move along the same path toward a shared goal.
A development plan should never be fixed or permanent. It must evolve alongside the work environment and organizational culture. Employees should maintain an open mind and a positive attitude toward updating their plans. Key elements that require regular updates include:
- Flexible Goals: Goals must remain adaptable to changing situations and market needs. They should be reviewed and updated regularly to remain relevant.
- Adaptable Skill Sets: You must continuously update your skills based on your goals and current requirements. Adaptability is essential in today’s shifting professional landscape.
- Dynamic Timelines: Timelines should change according to company priorities. You must be able to identify your top priorities and adjust your schedule as organizational needs shift.
Summary
Professional development represents a strategic, planned effort by an organization to improve its overall effectiveness and health while facilitating meaningful career transitions. The primary objective of professional development is to build an individual’s career while increasing their contributions to the organization, ensuring that results are achieved smoothly and efficiently.
Success in an organization requires a combination of hard work, a commitment to continuous learning, and flexibility regarding timelines. A lack of up-to-date knowledge or an outdated understanding of work procedures can be detrimental to both the individual and the company. Therefore, it is essential to remain a lifelong learner and a dedicated contributor.
To stay competitive, you must update your skills daily to keep pace with emerging technologies. You must always be prepared to embrace changes and tackle new challenges within the work culture. Ultimately, professional development is about mastering the processes and planning required to successfully navigate the human side of organizational change.