Abstract
This paper talks about how to start a career in Human Resources (HR), focusing on entry-level jobs that help you build your skills and grow.
It explains why HR is important in companies, helping to hire the right people, follow workplace rules, and support the company’s success.
The main goals are to understand what entry-level HR jobs involve, the skills you need to do well, and how these roles can lead to bigger career opportunities.
To understand how these roles evolve into strategic leadership opportunities, explore our in-depth article on Core HR Roles and Trends in 2025.
The research looks at different ways to get into HR, like education, HR certifications, internships, or even switching from other fields.
The findings show how technology is changing HR, making tasks easier and smarter with tools like artificial intelligence (AI). It also highlights the importance of creating diverse and inclusive workplaces and adjusting to remote or hybrid work styles.
People starting in HR help with hiring, building good relationships with employees, and managing HR data, which are all crucial to success in the role.
The paper suggests that combining tech skills, personal qualities like good communication, and a commitment to learning is the best way to succeed in HR.
It also points to exciting areas for future exploration, like how AI will shape HR, managing remote teams, and making workplaces more inclusive.
Introduction
Overview of Human Resources (HR)
Human Resources (HR) is a critical function within organizations that focuses on managing people and their potential.
It encompasses a wide range of activities, including recruitment, talent acquisition, employee relations, compensation and benefits, performance management, training and development, and organizational development.
HR professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring that an organization has the right people, in the right roles, at the right time, to achieve its strategic goals.

HR and Its Importance in Organizations
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: HR is responsible for attracting top talent, developing their skills, and creating a positive work environment that encourages employee engagement and retention.
- Managing Employee Relations: HR professionals build strong relationships with employees, address concerns and grievances, and promote a fair and equitable workplace.
- Ensuring Compliance: HR ensures that the organization complies with all relevant labor laws and regulations, such as equal employment opportunity, workplace safety, and employee privacy.
- Supporting Organizational Strategy: HR aligns its activities with the organization’s strategic goals, ensuring that the workforce has the necessary skills and capabilities to drive success.
- Managing Change: HR plays a critical role in managing organizational change, such as mergers, acquisitions, and restructuring, by effectively communicating with employees and minimizing disruption.
Purpose of the Paper
This paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of entry-level HR positions and the pathways to starting a career in HR. It explores the various career options available in HR and the key skills and knowledge required for success.
By understanding the fundamentals of HR and the opportunities it offers, aspiring HR professionals can make informed decisions about their career paths.
Why Understanding Entry-Level HR Positions Is Important
Understanding entry-level HR positions is crucial for several reasons:
- Laying the Foundation: Entry-level positions provide a solid foundation in HR principles and practices, allowing individuals to develop the necessary skills and knowledge for future advancement.
- Gaining Practical Experience: Entry-level roles offer opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, building practical experience and honing skills.
- Networking and Mentorship: Entry-level positions allow individuals to network with experienced HR professionals, learn from their expertise, and build valuable relationships.
- Career Progression: Entry-level positions serve as stepping stones to more senior HR roles, enabling individuals to advance their careers and take on greater responsibilities.
Research Objectives
This paper aims to achieve the following objectives:
- Understanding Pathways to Start in HR: Explore the various pathways to starting a career in HR, including education and certification requirements, internships, and entry-level positions.
- Exploring HR Career Options: Identify the diverse career options available within the HR field, such as generalist HR, specialist HR, HR Coordinator, and HR consulting.
- Identifying Key Skills Needed: Determine the essential skills and knowledge required for success in entry-level HR positions, including communication, problem-solving, critical thinking, and HR-specific expertise.
Structure of the Paper
This paper is structured as follows:
- Introduction: Provides an overview of HR, the purpose of the paper, the research objectives, and the structure of the paper.
- Literature Review: Reviews existing research on entry-level HR positions, career paths, and key skills.
- Methodology: Describes the research methodology used to collect and analyze data.
- Findings and Analysis: Presents the findings of the research, including insights into entry-level HR positions, career options, and key skills.
- Discussion and Implications: Discusses the implications of the findings for aspiring HR professionals and organizations.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the key findings and recommendations for further research.
This paper aims to provide valuable insights into the world of HR for aspiring professionals and organizations seeking to build and develop their HR teams.
Literature Review: Unveiling the Roots and Evolution of HR
From Record-Keeping to Strategic Partner: HR’s Fascinating Journey
The evolution of HR as a distinct profession is closely tied to the Industrial Revolution. Initially, HR functions were rudimentary, primarily focused on record-keeping and transactional tasks. As organizations grew in size and complexity, the need for more strategic HR practices emerged.
Origins and Evolution of HR Roles
The early 20th century witnessed the birth of personnel departments. These departments handled essential tasks like recruitment, compensation, and navigating employee relations.
However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that HR truly established itself as a strategic partner to the business.
With globalization and technological advancements accelerating, HR’s role expanded to encompass talent management, organizational development, and change management, becoming a driving force for success.
The HR landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and changing workforce demographics.
Focus on Technology
Technology has revolutionized HR practices. HR professionals now leverage HR technology solutions to automate routine tasks, analyze data, and make data-driven decisions. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data are reshaping the way HR operates.
Diversity and Inclusion
Diversity and inclusion have become top priorities for organizations. HR plays a pivotal role in fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace, attracting and retaining talent from diverse backgrounds, and promoting equal opportunities.
Remote Work
The increasing adoption of remote work has presented new challenges and opportunities for HR. HR professionals must adapt to managing remote teams, ensuring employee engagement, and maintaining a strong company culture in a dispersed workforce.
The Role of Entry-Level HR Positions
Entry-level HR positions serve as a crucial stepping stone for aspiring HR professionals. These roles provide valuable experience and exposure to various HR functions, allowing individuals to develop their skills and knowledge.
Contribution to Organizational Goals and Development
Entry-level HR professionals contribute to organizational goals by:
- Streamlining Recruitment and Selection: They assist with sourcing and screening candidates, conducting interviews, and onboarding new hires, ensuring the organization acquires top talent.
- Facilitating Smooth Employee Relations: They provide administrative support for employee relations activities such as grievance handling and disciplinary processes, promoting a harmonious work environment.
- Managing HR Data Effectively: They maintain accurate employee records, generate reports, and analyze HR data, providing crucial insights for informed decision-making.
- Supporting Training and Development: They assist in organizing training programs, conducting needs assessments, and tracking employee development, ensuring the workforce possesses the necessary skills to excel.
Skill and Competency Requirements in HR
To succeed in HR, professionals need a combination of technical skills and soft skills.
Key Skills from Past Research or Industry Studies
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for building relationships, resolving conflicts, and conveying information clearly.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex problems, identify solutions, and make informed decisions.
- Interpersonal Skills: Strong interpersonal skills are necessary for building rapport with employees, managers, and stakeholders.
- Organizational and Time Management Skills: The ability to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and manage multiple projects simultaneously.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in HR software, data analysis, and technology tools.
- Business Acumen: Understanding of business operations, financial principles, and strategic HR planning.
- Ethical Conduct: Adhering to ethical principles and maintaining confidentiality.
By cultivating these skills and competencies, entry-level HR professionals can establish themselves as valuable assets, contribute to organizational success, and pave the way for a rewarding career path.
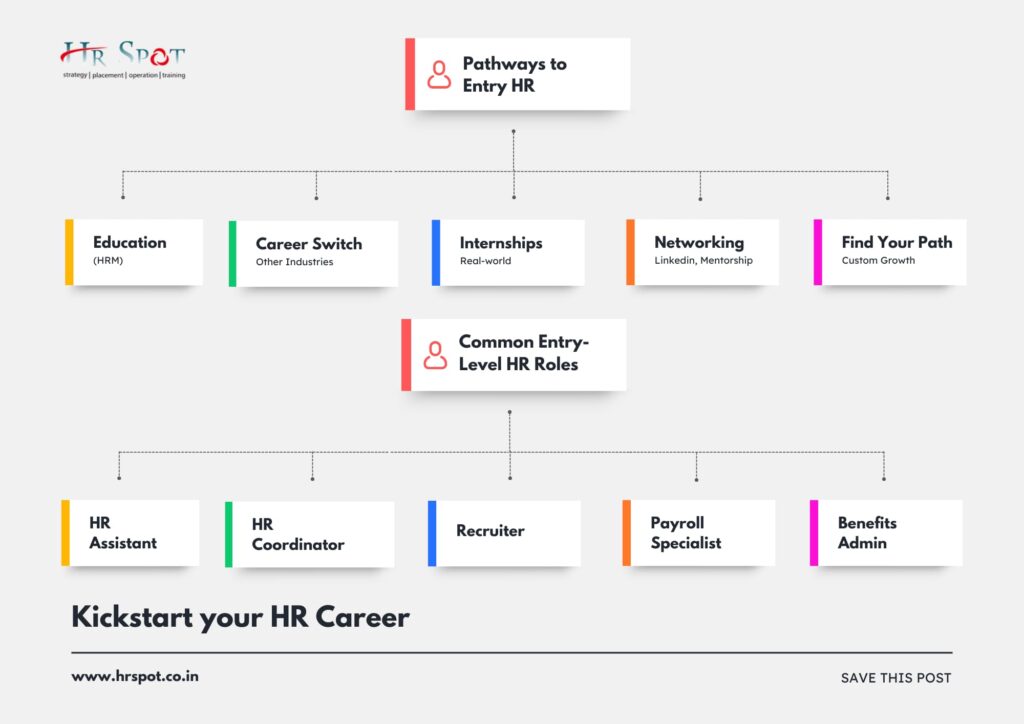
Pathways to Start a Career in HR
1. Education Requirements
Formal education is a common route for aspiring HR professionals. A bachelor’s degree in Human Resources Management (HRM) or a related field like Business Administration, Psychology, or Sociology can provide a strong foundation.
- Master’s Degree: While not always necessary, a master’s degree in HRM or a related field can enhance career prospects, particularly for those aiming for senior leadership roles.
- Certifications: Certifications like the HR Leadership Course, Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Certified Professional (SHRM-CP) or Senior Certified Professional (SHRM-SCP) can validate expertise and open doors to new opportunities.
- Courses and Training: Online courses and workshops can supplement formal education and provide specialized knowledge in areas like recruitment, compensation and benefits, employee relations, and labor law. For more on which training or certifications matter, see Things To Do For A Successful HR Career.
2. Alternative Pathways
Experience in other fields can be a surprising asset in HR. Professionals from sales, management, or customer service often possess transferable skills like communication, problem-solving, and relationship-building— all crucial for HR success.
Those with experience in these areas can leverage their existing skills for a smooth transition into HR by seeking entry-level positions or pursuing relevant certifications and training.
Additionally, many organizations offer career-change programs or internal mobility opportunities to help individuals transition into HR roles.
3. Internships and Training Programs
Internships and training programs provide invaluable hands-on experience and exposure to the day-to-day operations of HR departments.
- Internships: Internships allow students to gain practical experience, network with HR professionals, and build a portfolio of projects. They can also lead to full-time job offers upon graduation.
- Training Programs: Companies often offer training programs for new HR hires, providing them with the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in their roles.
Importance of Practical Experience: Hands-on experience is crucial for developing the skills and knowledge needed to excel in HR. Internships and training programs provide opportunities to learn from experienced professionals and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations.
4. Building Your Network
Building a strong professional network is key to career advancement in HR. Here’s how to unlock the power of networking:
- Leveraging LinkedIn: LinkedIn is a powerful platform for connecting with HR professionals, sharing insights, and discovering job opportunities.
- Alumni Networks: Utilizing alumni networks can help connect with former classmates who are working in HR and gain valuable insights into the industry.
- HR Associations: Joining professional HR associations like SHRM provides access to networking events, conferences, and mentorship programs.
- Mentorship: Mentorship can provide guidance, support, and career advice from experienced HR professionals.
5. Finding Your Path
There are multiple pathways to a successful career in HR. Whether through formal education, experience in other fields, internships, training programs, or networking, individuals can find their own unique path to success in this dynamic and rewarding field.
Types of Entry-Level HR Positions
Common Entry-Level HR Roles
There are several common entry-level HR roles that can serve as a starting point for a career in human resources:
- HR Assistant: HR assistants provide administrative support to HR departments. Their duties typically include maintaining employee records, processing paperwork, scheduling appointments, and answering employee inquiries.
- HR Coordinator: HR coordinators handle a wider range of HR tasks, including onboarding new employees, managing employee benefits, and coordinating training programs. They may also assist with recruitment and selection processes.
- Recruiter or Talent Acquisition Specialist: Recruiters and talent acquisition specialists are responsible for sourcing, screening, and interviewing potential candidates. They may also use various recruitment tools and techniques to attract top talent.
- Payroll Specialist: Payroll specialists manage the payroll process, including calculating wages, processing taxes, and ensuring compliance with labor laws. They may also handle employee benefits administration and reporting.
- Benefits Administrator: Benefits administrators manage employee benefits programs, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and flexible spending accounts. They may also assist employees with enrollment, claims, and eligibility issues.
Beyond the Job Description
To gain a deeper understanding of these roles, explore job descriptions and postings. These documents provide detailed information about the specific skills, experience, and qualifications sought for each position.
Sectors Hiring Entry-Level HR Professionals
Entry-level HR professionals are in demand across various industries. Here are some sectors that frequently recruit entry-level HR talent:
- Healthcare
- Technology
- Finance
- Education
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Government
- E-commerce
The demand for HR professionals varies by industry and location. However, as businesses continue to grow and evolve, the need for skilled HR professionals is expected to remain strong.
Additional Tips for Success
- Gain Practical Experience: Internships and volunteer opportunities provide invaluable hands-on experience and allow you to network within the HR field.
- Stay Current: Commit to continuous learning and professional development to stay updated on the latest HR trends and best practices. Resources such as online courses or professional association memberships can be helpful.
- Build Your Network: Cultivate relationships with HR professionals through industry events, online platforms like LinkedIn, or alumni networks. This can open doors to new opportunities and provide career guidance. You can also use tools like HR Job Employability Score & HR Salary Eligibility Checker to gauge where you stand.
By understanding the different types of entry-level HR positions and the industries that hire HR professionals, you can take the first step toward a successful career in human resources.
Exploring HR Career Pathways
1. Advancing Your HR Career
HR professionals have the potential to ascend the HR career ladder, progressing from entry-level positions to strategic leadership roles.
This journey is often fueled by gaining practical experience, acquiring specialized certifications like PHR, SPHR, or SHRM-CP, and pursuing continuous learning.
As you climb the HR ladder, you’ll assume greater responsibility, including managing teams, overseeing projects, and making strategic decisions that impact the organization’s success.
2. Specialized HR Functions
Within the HR domain, there are several specialized functions that professionals can focus on. These include:
- Talent Management: Involves attracting, recruiting, selecting, and onboarding top talent. Talent managers focus on creating a positive employee experience, developing talent pipelines, and implementing effective performance management systems.
- Employee Relations: HR professionals in this area handle employee grievances, conduct investigations, and ensure compliance with labor laws. They play a crucial role in maintaining harmonious relationships between employees and the organization.
- Training and Development: These professionals design and deliver training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge. They may also facilitate leadership development initiatives and career progression planning.
- Compensation and Benefits: HR professionals in this function are responsible for designing and administering compensation and benefits packages. They analyze market trends, conduct salary surveys, and ensure compliance with tax and regulatory requirements.
- HR Analytics: This emerging field involves using data to make informed HR decisions. HR analysts leverage data to measure the effectiveness of HR programs, identify trends, and predict future workforce needs. If you’d like formal training, check out the HR Analytics Course to get you started.
3. Leadership Roles in HR
Executive-Level Positions
- Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO): The top HR executive responsible for overseeing all HR functions and aligning HR strategies with overall business goals.
- Chief People Officer (CPO): A broader role that encompasses HR, talent management, and organizational development.
Senior Leadership Positions
- Vice President of Human Resources: Oversees the HR department and reports directly to the CEO or COO.
- Director of Human Resources: Manages a specific HR function or a particular division within the organization.
Other Leadership Roles
- HR Business Partner: Works closely with specific business units to provide HR support and strategic advice.
- Head of Talent Acquisition: Leads the recruitment and hiring process.
- Head of Learning and Development: Oversees employee training and development programs.
- Head of Compensation and Benefits: Manages compensation and benefits programs.
- Head of Employee Relations: Handles employee relations issues, such as grievances, disciplinary actions, and investigations.
It’s worth noting that HR leadership roles can vary depending on the size and industry of the organization. As HR becomes increasingly strategic, new leadership positions may emerge, such as Chief Diversity Officer or Chief Experience Officer.
The Dynamic Nature of HR
The HR career landscape offers a multitude of opportunities for individuals with diverse skills and interests. By specializing in specific HR functions, pursuing advanced certifications, and gaining relevant experience, HR professionals can carve out successful and fulfilling careers.
Whether you aspire to become a talent management expert, an employee relations specialist, a training and development guru, a compensation and benefits specialist, an HR analyst, or an HR leader, the HR field provides a platform for growth and impact.
For tips on getting your first HR role—even from another domain—see Simplest Way to Get an HR Job for Fresher or Experienced.
Challenges and Opportunities in Entry-Level HR Careers
Common Challenges
Lack of Practical Experience: New HR professionals often face challenges due to their limited hands-on experience. To overcome this, they should seek opportunities to shadow experienced HR professionals, attend workshops, and actively participate in projects to gain practical insights.
Conflict Management: Conflict management is key for HR professionals, especially entry-level ones. They may handle disputes between employees or with management.
Strong communication, active listening, and staying calm can help resolve issues. Understanding the company’s culture also helps spot potential triggers and prevent conflicts.
Multitasking and Time Management: HR professionals juggle multiple responsibilities at once, such as welcoming new employees, resolving issues, and processing departures. To manage everything effectively, they need to:
- Plan Tasks: Decide which tasks are most important and complete those first.
- Share the Work: Delegate tasks when possible.
- Use Time Wisely: Try techniques like:
- Time Blocking: Setting aside specific times to focus on each task.
- Pomodoro Technique: Working for 25 minutes, then taking a 5-minute break.
Being organized and paying close attention to details are also essential for completing tasks accurately and on time.
Other Challenges in Entry-Level HR Careers Include:
- Managing diverse responsibilities like recruitment, onboarding, and compliance.
- Meeting tight deadlines while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
- Balancing employee needs with organizational goals.
- Limited decision-making authority in critical situations.
- Navigating workplace dynamics and building credibility as a new professional.
Opportunities for Growth
Upskilling Through Certifications: Obtaining HR certifications like PHR or SHRM-CP can significantly boost the credibility and career prospects of entry-level HR professionals.
These certifications validate knowledge and skills in various HR domains, including recruitment, employee relations, compensation, and benefits.
By investing in certifications, new HR professionals can differentiate themselves and position themselves for future advancement.
Leveraging HR Technology: The HR industry is increasingly adopting technology and software solutions. Entry-level HR professionals who are proficient in HR technology can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions.
Learning to use HRIS systems, applicant tracking systems, and other HR tools can enhance their value to organizations and prepare them for leadership roles. Staying updated on emerging HR trends and technologies is crucial to remain competitive and relevant in the field.
Opportunities in Entry-Level HR Careers:
- Developing core HR skills like communication, conflict resolution, and policy management.
- Gaining exposure to various HR functions for specialization opportunities.
- Establishing a strong foundation for career growth in a high-demand field.
- Learning about organizational culture and employee engagement strategies.
- Building a network of professional contacts within the organization and industry.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Key Findings
- Technological Transformation
HR roles are increasingly shaped by technology and data analytics, making them more strategic and dynamic. - Importance of Soft Skills
Despite the rise of technical skills, soft skills like communication, adaptability, and empathy remain essential for HR success. - Diversity and Inclusion
The study highlights the critical need to foster diverse and inclusive workplaces, aligning with global efforts to achieve equity. - Emerging Trends
Aspiring HR professionals must stay updated on trends such as remote work, employee wellness programs, and AI integration in HR functions. - Workforce Evolution
These findings provide insights into how HR practices are adapting to meet the demands of the future workforce.
Actionable Steps
Develop a Versatile Skill Set
- Build a foundation in business and psychology to understand organizational behavior and employee needs.
- Gain technical expertise to complement traditional HR knowledge.
Earn Relevant Certifications
- Pursue certifications like SHRM-CP or PHR to enhance credibility and demonstrate specialized HR knowledge.
Leverage Networking Opportunities
- Connect with HR professionals through industry events, seminars, and social platforms to gain mentorship and discover job opportunities.
- Engage in professional associations or HR communities for continued support and learning.
Embrace HR Technology
- Learn to use HR platforms like Workday, BambooHR, Keka, or other management tools to handle recruitment, payroll, and analytics effectively.
- Stay updated on emerging tech trends such as AI in HR processes.
Understand Employment Laws and Compliance
- Acquire knowledge of labor laws and workplace regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal pitfalls in HR practices.
Develop Emotional Intelligence and Problem-Solving Skills
- Strengthen soft skills to resolve conflicts, foster collaboration, and create a positive workplace environment.
- Be empathetic and adaptive to meet the diverse needs of employees and organizational goals.
Engage in Continuous Learning
- Attend webinars, conferences, and training sessions to stay informed on the latest HR trends.
- Read industry publications to stay updated on best practices, remote work strategies, and innovative employee engagement methods.
By following these actionable steps, aspiring HR professionals can establish a strong foundation and thrive in this dynamic career field.
Future Research Suggestions
The research has provided valuable insights into the field of human resources (HR), but there are still several areas that need deeper exploration to understand the full scope of HR’s evolving role:
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on HR Roles
With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), there is an opportunity to study how AI will reshape the responsibilities of HR professionals. Questions like how AI can improve recruitment, employee performance tracking, and workforce analytics need further exploration. Moreover, researchers could analyze whether AI will fully replace certain HR tasks or work as a support system to make HR functions more efficient.
Hybrid Work Models
The transition to hybrid work—where employees split their time between remote and in-office work—has introduced both opportunities and challenges.
Future research could focus on understanding the long-term effects of this model on employee engagement, productivity, and retention.
Additionally, studies could identify best practices to balance flexibility with organizational goals, ensuring both employee satisfaction and business success.
Leadership in the Age of Automation
As automation becomes more prevalent in workplaces, leadership roles and skills are evolving. Research could explore what leadership competencies will be essential in managing teams that include both humans and automated systems. For instance, how will leaders inspire creativity and teamwork when repetitive tasks are handled by machines?
Cultural Diversity and Team Dynamics
Cultural diversity in the workplace has a significant impact on team dynamics and organizational success. Future studies could examine how diverse teams can leverage their unique perspectives to enhance innovation and problem-solving.
It’s also important to research how organizations can overcome challenges like cultural misunderstandings and unconscious bias to create inclusive environments.
By addressing these areas, future research can provide deeper insights into how HR can adapt to technological advancements, changing work environments, and evolving leadership needs in today’s fast-paced world.
References
- SHRM India Corporate Information
- UCD Professional Academy, University College Dublin
- Indeed Editorial Team
- AIHR Academy To Innovate HR
- Engagedly Inc., USA
- Bay Atlantic University, Washington, D.C.
- Acacia Limited, ICS Learn Group, UK
- CareerVillage
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- Shrofile, India
- ZDNET, A Ziff Davis Company
Appendices
1. Graphs & Statistics on HR Job Growth (Supplementary Data)

The HR professional services market has seen significant growth recently. It is projected to increase from $7.78 billion in 2025 to $13.66 billion in 2029, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.03%.
Several factors have contributed to this expansion, including regulatory changes, economic shifts, globalization, demographic trends, talent shortages, and crisis management.

Acknowledgments
I express my heartfelt gratitude to HR Spot Institute for their invaluable support and resources, enabling the successful completion of this research.
A special thanks to my mentors, peers, and instructors for their insightful guidance and encouragement throughout this journey. Your expertise and constructive feedback have been instrumental in shaping the outcomes of this work.
Lastly, I extend my appreciation to the authors and organizations whose work provided foundational knowledge and inspiration for this study. Your contributions to the HR field have been enlightening and motivational.

